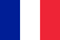
Papillomas on the body are benign formations of an infectious nature. Predominantly 16 and 18 strains have a tendency to degenerate into malignant forms (more than 100 species are known in total). Wart and papilloma are synonymous.
Characteristics of the disease:
- It occurs in people of any age, mainly in women (the number of detected cases is 1. 5 times higher than in men).
- Infection occurs through household contact or sexual contact. It goes unnoticed for a long time, because the virus does not have a strong effect on the immune system. In addition, after entering the genome, only the viral DNA remains, and not the virus itself (it is almost impossible to remove it).
- There are a number of vaccines designed to reduce infections and reduce susceptibility to viral agents.
- Immunity after infection is formed type-specific, non-cross, stress-free, low, which means the possibility of re-infection.

Causes
The main reason for the appearance of papillomas on the body is the human papilloma virus (HPV, papilloma virus). It belongs to the viruses that contain DNA, which explains its ability to integrate into the human genome and change its structure. The virus enters the bloodstream through microdamages and deposits on the basal layer of the epidermis. Division occurs only at the germ level, in others the virus can be detected, but there is no division at these levels.
There are several clinical forms of the disease:
- manifest - primary infection with the virus in persons with reduced immunity;
- subclinical - a form in which manifestations of this pathology periodically occur, followed by long-term relapses;
- latent - a form associated with the direct integration of the virus into the genome (carrier).
Predisposing factors in the development of neoplasms:
- Skin damage. The virus cannot enter the bloodstream without at least minimal damage to the skin, which serves as the gateway to infection.
- Decreased immunity. HPV can be attributed to conditionally pathogenic viruses, which makes it dangerous for humans in case of suppression of the normal cellular or humoral immune response.
- Non-compliance with hygiene rules when visiting public places. The virus is contagious, and infection can occur even at low concentrations in the environment.
- Violation of normal diet, constant stress and lack of proper rest lead to suppression of the immune system, the body becomes vulnerable to the action of pathogens.
- Frequent inflammatory and infectious diseases lead to exhaustion of the immune system (this is especially important for people who are often ill).
- Human papilloma virus can also be transmitted from mother to child at birth (vertical transmission).
External manifestations
External manifestations of papillomas in the photograph have the following characteristics:
- Multiple formations protruding above the surface of the skin. They can have the shape of a classic wart (a flat lesion on a broad stem) or have a thin stem and hang over the skin like a rooster comb.
- The color rarely differs from the surrounding tissues. Exceptions are cases of germination of the formation in the superficial vascular network, in which case it takes on a reddish hue. A rapid change in color signals a possible rebirth (differentiation with moles is also performed).
- The contour is usually smooth and clear. The exceptions are formations that have degenerated into a tumor.
- The surface is often smooth and slightly shiny. In the case of the location in the area of the upper lids, neck, armpits, the surface is often uneven with pointed elevations like cauliflower.
- The diameter ranges from small foci from a few millimeters to 1-2 cm. Formations of different calibers may be present on the same part of the human body. If the papilloma grows too fast, you need to consult a doctor.
How to get rid of papillomas
Treatment of papillomas on the body is carried out according to one scheme, regardless of the exact location (for each type there is an optimal option or combination):
- Destructive methods (physical and chemical).
- Combined techniques (simultaneous action of local drugs and the possibility of destructive treatment).
It is allowed to treat papillomas with cytotoxic and immunological preparations only under the condition of the overall process (papillomatosis, ie a very large number of papillomas on the body). In cases with individual formations, such therapy is not carried out due to the large number of side effects and cross-reactions in drugs of these groups.
Methods of destruction
The possibilities of destructive treatment are the same for all types of skin lesions caused by HPV. They are divided into physical and chemical.
Methods of physical destruction:
> zxtable border = "1" cellpadding = "0" >Folk remedies
It is allowed to remove growths at home with traditional medicine, but it should be borne in mind that their efficiency is low. In addition, before starting such treatment, it is necessary to consult a specialist in order to distinguish papillomas from a number of other skin diseases with similar manifestations.
> zxtable border = "1" cellpadding = "0" >Crush a few flowers in mortar, apply the resulting mixture on the affected area and fix for 30 minutes. Repeat the procedure in the morning and in the evening for 21 days.